DERMCUP

HIGH RESOLUTION ULTRASOUND SCANNER FOR DERMIS
Thanks to its high frequencies (25MHz & 50MHz), DERMCUP offers a high resolution:
Axial : 30 µm
Lateral : 120 µm
For dermatology, it is necessary to visualize infracentimeter lesions. This cannot be done with traditional ultrasound scanner fitted with 7 to 13 MHz probes.
DERMCUP is well adjusted for visualization of lesions in dermis.
Features & Benefits
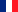
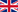
Dermis in pictures
The Dermcup allows the acquisition in real time and in-vivo of high resolution skin vertical cross sections.
Dermis is echogenic. The echoes come from the network of collagen fibers and elastic fibers.
The lesions (tumors, cysts, angiomas) have a hypoechoic appearance.
Ergonomic and very hand probe

The probe has a 16 mm exploration length. That is remarkable.
It is very handy because of its compactness.
2D or 3D probe.
Image post-processing software
Atys in collaboration with Creatis (biomedical imaging research laboratory: www.creatis.insa-lyon.fr) through AtysCrea Labcom has developped a powerful sotfware that performs the segmentation of structures that are present in the dermis (tumors, ...).
A version of the 3D viewer is available on demand (click here to contact Atys).
Tumor

Acne

Skin aging

Image library
Melanoma
Impairment of the horizontal structure of the skin with the presence of a homogeneous very hypoechoic lesion.
Ulcerated melanoma on the forearm infiltrating the dermis (the histological thickness was 3.7 mm, measured at 3.68 mm on echography image).).
Melanoma of the ear
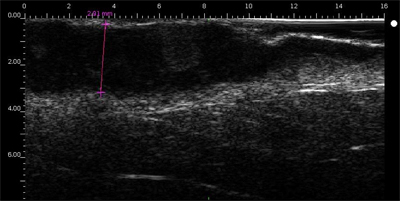
Basocellular carcinoma
Basocellular carcinoma on the forehead (above the temporal artery)
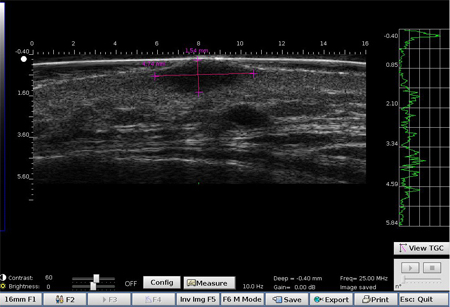
Basocellular carcinoma on the face above the mastoid

Superficial carcinoma

Pigmented carcinoma

Compound nevus of the dermis
Hypoechoic lesion with many echoes and margins with adjacent dermis not well-defined

Histiocytofibroma
Hypoechoic homogeneous dermal lesion with poorly-defined margins
 | 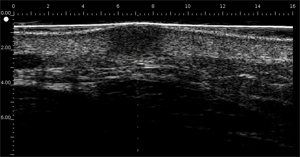 |
Seborrhoeic keratosis
Superficial lesion with often prominent entry echo line due to superficial keratose
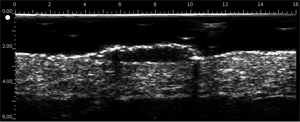
Epidermal cyst
Lesion often round, well-defined with inside strong echoes parallel to the surface

Sub-epidermal bubble
Anechoic lesion with thin hyperechoic line in the dermal surface demonstrating its sub-epidermal situation